本文最后更新于:2025年1月12日 凌晨
早期我已经在本地搭建了一个两台机器的k3s集群,并部署了Crawlab ( 一个使用Golang 开发的分布式爬虫管理平台),实现了本地的分布式集群服务环境的搭建。服务起来以后,动态的控制容器节点,监控容器运行状态,实现即使的扩容,这都需要我们Kubernetes进行控制。幸运的是Kubernetes直接提供了python、golang的客户端,可以方便的实现Kubernetes API 操作。所以接下来我们一起熟悉一下,基于golng客户端Kubernetes控制。
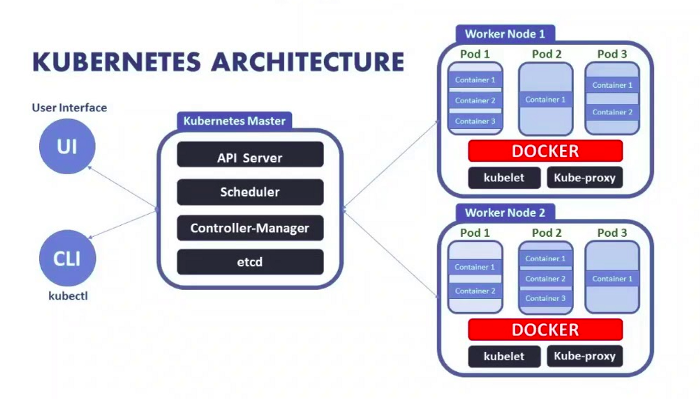
起步 访问 API 和查看列表 在了解 Kubernetes 的基本架构和提供 API 的方式后,接下来我们需要知道 Kubernetes 到底提供了哪些 API。为了方便调试,首先我们需要在本地运行 kubectl proxy 命令,kube-apiserver 就会在本地的 8001 端口上进行监听,也就是提供了一个 Kubernetes API 服务的 HTTP 代理。
这个时候我们可以访问:
1 $ curl https://127.0.0.1:6443/api/v1
查看所提供的对应 API‘s:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 {
访问 api/v1/pods 路径,获取所有 Pods
1 $ curl https://127.0.0.1:6443/api/v1/pods
访问结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 {"kind" : "PodList" ,"apiVersion" : "v1" ,"metadata" : {"selfLink" : "/api/v1/pods" ,"resourceVersion" : "614376" "items" : ["metadata" : {"name" : "awesome-project-76788db95b-7ztwr" ,"generateName" : "awesome-project-76788db95b-" ,"namespace" : "default" ,"selfLink" : "/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/awesome-project-76788db95b-7ztwr" ,"uid" : "4fdb6661-edbd-4fc6-bf71-1d2dadb3ffc1" ,"resourceVersion" : "608545" ,"creationTimestamp" : "2020-05-03T02:29:32Z" ,"labels" : {"app" : "awesome-project" ,"pod-template-hash" : "76788db95b" ...
更多的 API 列表和介绍可查看官方文档 。
Kubernetes 官方提供了 Go 语言的 Client SDK,也就是client-go
SDK集群外访问: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 package mainimport ("context" "flag" "fmt" "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1" "k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes" "k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd" "os" func main () var kubeconfig *string "kubeconfig" , "/etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml" , "absolute path to the kubeconfig file" )"" , *kubeconfig)if err != nil {panic (err.Error())if err != nil {panic (err.Error())"" ).List(context.TODO(),metav1.ListOptions{})if err != nil {panic (err.Error())"There are %d pods in the k8s cluster\n" , len (pods.Items))"default" if err != nil {panic (err)"\nThere are %d pods in namespaces %s\n" , len (pods.Items), namespace)
kubeconfig默认是在/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf,由于我装的是K3s这里的路径是/etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml
执行程序
1 2 3 There are 15 pods in the k8s cluster5 pods in namespaces crawlab
SDK集群内访问 除以上方法外,还可以在 k8s 集群内运行客户端操作资源类型。既然是在 k8s 集群内运行,那么就需要将编写的代码放到镜像内,然后在 k8s 集群内以 Pod 方式运行该镜像容器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 # cat main2.go package mainimport ("fmt" "time" "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1" "k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes" "k8s.io/client-go/rest" func main () if err != nil {panic (err.Error())if err != nil {panic (err.Error())for {"" ).List(metav1.ListOptions{})if err != nil {panic (err.Error())"There are %d pods in the k8s cluster\n" , len (pods.Items))"default" if err != nil {panic (err)"\nThere are %d pods in namespaces %s\n" , len (pods.Items), namespce)for _, pod := range pods.Items {"Name: %s, Status: %s, CreateTime: %s\n" , pod.ObjectMeta.Name, pod.Status.Phase, pod.ObjectMeta.CreationTimestamp)if err != nil {panic (err)"\nThere are %d namespaces in cluster\n" , len (nss))for _, ns := range nss {"Name: %s, Status: %s, CreateTime: %s\n" , ns.ObjectMeta.Name, ns.Status.Phase, ns.CreationTimestamp)10 * time.Second)
该示例主要演示如何在 k8s 集群内操作 Pod 和 Namespaces 资源类型,包括获取集群所有 Pod 列表数量,获取指定 Namespace 中的 Pod 列表信息,获取集群内所有 Namespace 列表信息。这里,该方式获取 k8s 集群配置的方式跟上边方式不同,它通过集群内部创建的 k8s 配置信息,通过 KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST 和 KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT 环境变量方式获取,来跟 k8s 建立连接,进而来操作其各个资源类型。如果 k8s 开启了 TLS 认证方式,那么默认读取集群内部指定位置的 tokenFile 和 CAFile。
编译一下,看下是否通过。
1 2 3 # go build main2.go go
接下来,在同级目录创建一个 Dockerfile 文件如下
1 2 3 FROM debian
构建docker镜像
1 2 3 4 # ls # docker build -t client-go/in-cluster:1.0 .
因为本机 k8s 默认开启了 RBAC 认证的,所以需要创建一个 clusterrolebinding 来赋予 default 账户 view 权限。
1 2 $ kubectl create clusterrolebinding default-view --clusterrole =view --serviceaccount =default:default .rbac .authorization .k8s .io "default-view" created
最后,在 Pod 中运行该镜像即可,可以使用 yaml 方式或运行 kubectl run 命令来创建。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 # kubectl run --rm -i client-go -in-cluster-demo --image=client-go /in-cluster:1.0 --image-pull-policy=Never3 pods in namespaces default go -in-cluster-demo-58 d9b5bd79-7 w5ds, Status: Running, CreateTime: 2019 -02 -13 14 :25 :38 +0000 UTC-7 b8c9bc5c9-64 g8k, Status: Running, CreateTime: 2019 -01 -10 14 :40 :18 +0000 UTC-7 b8c9bc5c9-bx7ml, Status: Running, CreateTime: 2019 -01 -10 14 :40 :18 +0000 UTC5 namespaces in cluster2019 -01 -10 09 :01 :52 +0000 UTCdefault , Status: Active, CreateTime: 2019 -01 -05 09 :18 :02 +0000 UTC2019 -01 -05 09 :18 :02 +0000 UTC2019 -01 -05 09 :18 :02 +0000 UTC2019 -01 -08 15 :00 :41 +0000 UTC16 pods in the k8s cluster
运行正常,简单验证一下吧!
1 2 3 4 5 NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEclient -go-in-cluster-demo-58 d9b5bd79-7 w5ds 1 /1 Running 0 10 mpodinfo -7 b8c9bc5c9-64 g8k 1 /1 Running 1 33 dpodinfo -7 b8c9bc5c9-bx7ml 1 /1 Running 1 33 d
SDK对k8s各资源对象操作 上边演示了,在 k8s 集群内外运行客户端操作资源类型,但是仅仅是 Read 相关读取操作,接下来简单演示下如何进行 Create、Update、Delete 操作。创建 main.go 文件如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 # cat main3.go package mainimport ("flag" "fmt" "k8s.io/api/core/v1" "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1" "k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes" "k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd" func main () var kubeconfig *string "kubeconfig" , "/etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml" , "absolute path to the kubeconfig file" )"" , *kubeconfig)if err != nil {panic (err)if err != nil {panic (err)"client-go-test" "Creating Namespaces..." )if err != nil {panic (err)"Created Namespaces %s on %s\n" , result.ObjectMeta.Name, result.ObjectMeta.CreationTimestamp)"Getting Namespaces..." )if err != nil {panic (err)"Name: %s, Status: %s, selfLink: %s, uid: %s\n" ,"Deleting Namespaces..." )if err := namespacesClient.Delete(name, &metav1.DeleteOptions{nil {panic (err)"Deleted Namespaces %s\n" , name)
执行程序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 # go run main3.go go -test on 2019 -02 -13 21 :44 :52 +0800 CSTgo -test, Status: Active, selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/client-go -test, uid: 8 a2de86e-2 f95-11e9 -b2e0-a0369f3f0404go -test